Table of contents
What Sitemap is and what it is used for
An XML sitemap is a file that serves as a blueprint to help search engines find, crawl and index the content of your website. Sitemaps also tell search engines which pages you own are the most important.
Main sitemap types:
There are several types of sitemaps:
- Normal XML sitemap: This is by far the most common type of sitemap. It is an XML-type file and contains a listing with different pages of the website.
- Video Sitemap: This is specifically used to help Google find the video content on your page.
- News Sitemap: Helps Google find content on sites approved for Google News.
- Image Sitemap: Helps Google find all the images hosted on the website.
Why it is important
The XML sitemap is a file that we can upload to Google Search Console to tell the Googlebot itself which parts of our website are most relevant and should be taken into account when indexing.
It acts as a list of priorities for the search engines facilitating their work.
In addition, there are some special cases where creating the sitemap is very useful.
You know that Google largely finds web pages through links.
If your web project is new and has only a handful of external links, then a sitemap will help you a lot to help search engines find your most relevant pages.
They are also very helpful when you have a web property with thousands of URLs.
Logically, not all URLs in your domain have inbound links from other websites.
In these cases, Google will have a hard time finding all those pages. That’s where sitemaps come into play: providing a complete list of the most important URLs on your website.
XML Sitemap Example
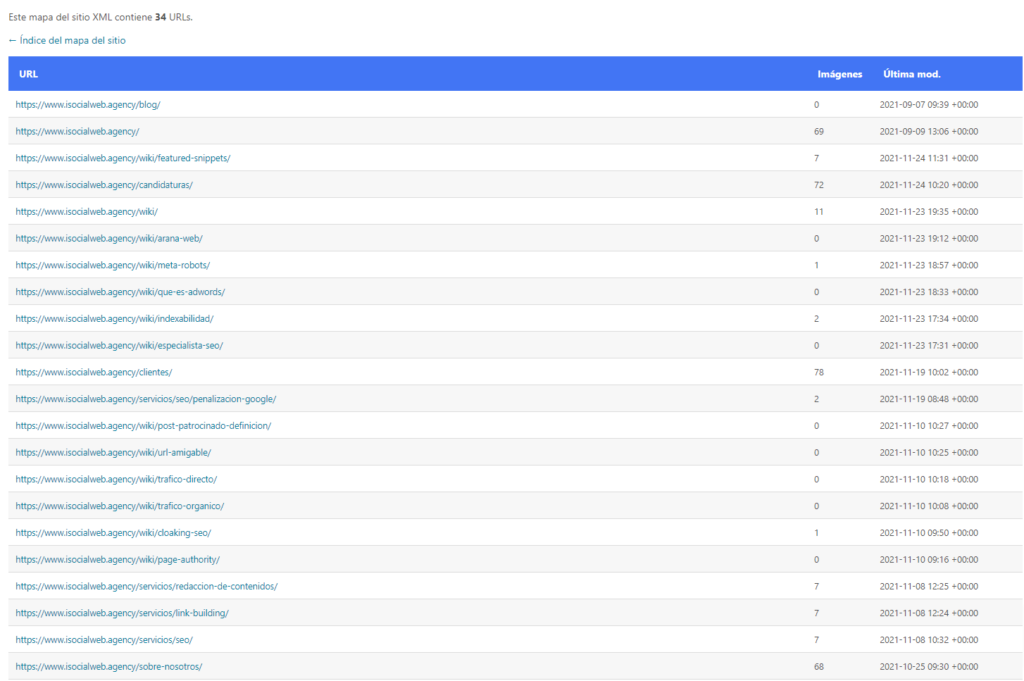
What Sitemap is and what it is used for
An XML sitemap is a file that serves as a blueprint to help search engines find, crawl and index the content of your website. Sitemaps also tell search engines which pages you own are the most important.
Main sitemap types:
There are several types of sitemaps:
- Normal XML sitemap: This is by far the most common type of sitemap. It is an XML-type file and contains a listing with different pages of the website.
- Video Sitemap: This is specifically used to help Google find the video content on your page.
- News Sitemap: Helps Google find content on sites approved for Google News.
- Image Sitemap: Helps Google find all the images hosted on the website.
Why it is important
The XML sitemap is a file that we can upload to Google Search Console to tell the Googlebot itself which parts of our website are most relevant and should be taken into account when indexing.
It acts as a list of priorities for the search engines facilitating their work.
In addition, there are some special cases where creating the sitemap is very useful.
You know that Google largely finds web pages through links.
If your web project is new and has only a handful of external links, then a sitemap will help you a lot to help search engines find your most relevant pages.
They are also very helpful when you have a web property with thousands of URLs.
Logically, not all URLs in your domain have inbound links from other websites.
In these cases, Google will have a hard time finding all those pages. That’s where sitemaps come into play: providing a complete list of the most important URLs on your website.
XML Sitemap Example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
< urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" >
<url >
<loc>http://www.example.com/</loc>
<lastmod>2005-01-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
</urlset>
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Sitemap?
The Sitemap xml of a web page is a file in the root domain that helps tell search engines which URLs are most important to your website. If you want to improve your SEO this is one of the fundamental requirements to comply with. Check out our guide to learn how to set it up.
Sitemap URL – Where is it?
The sitemap file is usually located at the root of the server with your domain name followed by this extension: example.com/sitemap_index.XML or example.com/sitemap.XML. If you need to check yours we suggest you try these endings with your domain.
Sitemap WordPress
A very easy way to create a sitemap in WordPress is by installing a similar Yoast SEO plugin. To do this go to the plugin section of your installation → Select new plugin → type “Yoast SEO” → Click “install”.
Create HTML sitemap?
HTML sitemaps are the equivalent of an XML sitemap… but for users. They are basically an HTML page with a list of the most important URLs of your website linked. They are used to improve internal linking.
